What is GLP-1?
- Glucagon Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist
- Hormone Created by Small Intestines
- Regulates blood sugar levels and appetite
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-like Peptide-1) medications mimic the natural hormone GLP-1
Primary Roles of GLP-1 Hormone and Drug
- Increase insulin
- Decrease glucagon
- Suppress appetite
- Slow stomach emptying
GLP-1 Effects
Pancreas:
⬆️ Insulin
⬇️ Glucagon
Stomach:
⬇️ Gastric emptying
⬇️ GI motility
Brain:
⬇️ Food intake
⬇️ Water intake
Mechanism of Action
- Stimulate insulin secretion after an oral glucose load via the incretin effect.
- Inactivated by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4).
- Delayed gastric emptying and inhibiting glucagon production from pancreatic α-cells if blood sugar levels are high.
- Can decrease pancreatic β-cell apoptosis while promoting their proliferation.
- Pharmacological levels of GLP-1 can revive insulin excretion.
Why It Matters?
GLP-1 drugs go beyond weight— they may protect your heart and liver too.
| Health Issue | GLP-1 Benefits |
|---|---|
| Type 2 Diabetes | Better blood sugar control |
| Obesity | Significant weight loss |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Reduced risk with some medications |
| Possibly in Future | NASH, PCOS, heart-specific outcomes |
These drugs are outperforming previous diabetes meds in both sugar and weight control (up to 20% weight loss).
Diabetes Prevalence Rate (%) in ASEAN Countries 2022
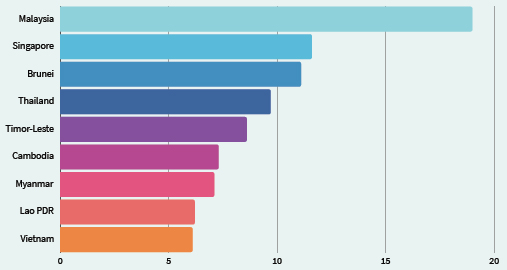
Source: (Word Data Bank, 2022)
Obesity Prevalence Rate (%) in ASEAN Countries 2022
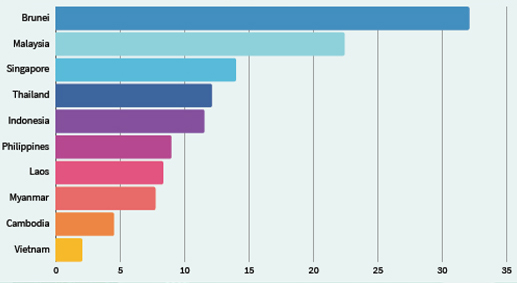
Source: (World Obesity Observatory, 2022)
What’s Next for GLP-1?
- Targeting Liver Diseases (NASH)
Clinical trials are assessing GLP-1 therapies for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). - More Heart-Focused Variants
Future treatments could see even greater cardiovascular benefits or new drugs that are designed specifically for heart health. - Personalized Medicine Using Genetic Profiling
Advances in genetic research and biomarkers may allow doctors to select the most appropriate GLP-1 treatment based on a patient’s genetic makeup. - Combo Therapies (GLP-1 + SGLT2 or DPP-4)
Future GLP-1 treatments could be combined with SGLT-2 inhibitors or DPP-4 inhibitors to create multi-action drugs.




