How the Proliferation of Digital Healthcare Information is Prompting Healthcare Players to Embrace Real-Time Data Management
It’s no secret that the world we live in today is full of data. From mobile phones to smart TVs, laptops to smart watches, there are a myriad of devices present in our lives today that track many our habits, preferences, and routines. The medical field has not escaped this phenomenon, with sensors and medical equipment recording almost every step in a patient’s journey including personal information, diagnoses, and even the impact a recommended course of treatment or medication has on any individual.
While this development can be heralded as a new era for patient management and a boost for healthcare players struggling to keep up with technology, it also brings about several issues for these facilities, with the key problem being: how do they keep up with all the data streams that are incoming?
The simple answer is an efficient data management system which incorporates the use of data analytics and self-learning AI models that can sift through, analyse, and harness the value of the data being collected for medical professionals to use. While in some other industries this process can be done retroactively, it is widely agreed that the healthcare field requires a real-time approach.
Two Key Factors that Make Data Management Work for Healthcare Professionals
1. A seamless and cohesive ecosystem
An efficient healthcare delivery process runs on being well-connected and comprehensive. Surgeons, clinicians, and interventionists all rely on connected sensors, surgical tools, radiology images and electronic medical records (EMRs) to provide the best care to their patient.
As such, a key must-have in managing healthcare data is the ability to identify the flow of data and the architecture of the system. Gaps, bottlenecks, or missing links between the abovementioned systems can cause issues including a broken chain of data, which will lead to data remaining stagnant in silos or on different systems and applications, thus causing the healthcare professional to be left with incomplete data on the patient’s condition or status.
To avoid this, healthcare institutions and their IT teams must ensure that the required data is easy to locate, easy to search, and easy to obtain as well as that it is useful (in the right format or units).
2. A connected framework
Accuracy in healthcare data is vital for doctors and nurses to make informed decisions on patient care. To foster this, healthcare facilities must have a platform with a connected framework in place that can identify sources of truth and ensure that that the relevant systems have jurisdiction over their corresponding data points.
The problem occurs when data that is readily available is re-entered unnecessarily, creating redundancies and therefore, inaccuracies. As the healthcare world transitions to using platforms, this issue occurs often, with a common error being receptionists/trainees manually entering a patient’s address when it is already available in their EMR.
As such, having connected data architecture (widely available through the right enterprise-class enterprise solution) can minimize the number of times these incidents happen, which then streamlines the flow of information for medical personnel; they will be able to glean additional context on the status of a patient and thus provide more informed care.
What a Real-Time Data Management Platform Can Offer Healthcare Facilities.
With the proliferation of medical data incoming, an effective platform takes historical and real-time data to predict trends, uncover insights, and drive medical advances, while ultimately fostering long-term growth. Broadly speaking, the platform should help medical teams provide better patient care and create a path to achieve medical breakthroughs.
Here are two key components of medical care that can benefit from real-time data management:
1. Decision-making
In the fast-paced world of patient care, having real-time data on hand can help physicians ask targeted and better questions of their patients, thus gathering a complete history and notes that can be studied by the care team. In turn, they will be able to make better clinical decisions for improving the patient’s health.
This data can then be fed back into the EMR and allow doctors to access the data electronically as well as improve their workflows. As a bonus, prompt and proactive actions by healthcare providers can prevent negative health outcomes and reduce the cost of care for patients.
2. Clinical trials and wearables
Data is also critical for those professionals monitoring clinical trials. It can be used to detect safety concerns for trial participants and caregivers can then intervene in a timely manner to stabilize the patient. The same holds true for wearables or medical devices that can track and monitor a patient’s progress; whether in a clinical trial or a course of treatment.
The Possibilities are Endless – Current Discussions around Data Management for Healthcare Facilities.
As briefly outlined in this article, data management and analysis are going a long way in helping the medical field accelerate its use of top-of-the-line technology which in turn improves the patient journey and the outcome of said process. On the operations side of things, organizations in this industry are also leveraging on these platforms to reduce overspending on stock management and ensuring the efficient deployment of staff and teams for various use cases. As time progresses and these processes are streamlined, there are a couple of key factors that healthcare professionals must be aware of when it comes to data management – structured vs. unstructured data, and data governance.
According to the World Economic Forum, the average hospital currently produces at least 50 petabytes of data each year; 80% of this data is unstructured, which means that it has to be normalized and standardized in order to be machine-readable. As such, medical facilities should look at how they’re managing data by conducting data governance. If carried out well and paired with the right modern data platform, this step will ensure that end users of the platform can readily access the data that they have permission to use in a format that is easily readable by the applications that they frequent; this in turn helps said end users make better business decisions.
In relation to structured and unstructured data, the 50 petabytes of data that hospitals produce each year comes in a variety of forms from a variety of sources. Additionally, according to the American Hospital Association, the amount of data being generated in healthcare is increasing at a rate of 47% annually. Collating and thus harnessing the value of this data is imperative for the entire data management exercise to make sense for hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare entities.
What is the difference between structured and unstructured data? Structured data refers to quantitative information, with examples being demographics, vital signs, billing codes, and medications. By contrast, unstructured data is not defined in its native format. Examples include clinical notes, problem lists, discharge summaries, and radiology reports.
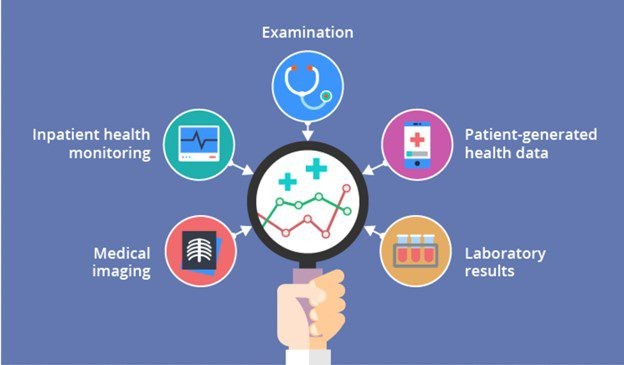
To ensure that both sets of data can help healthcare entities improve patient care and foster progress for their individual business, there are six basic steps to take:
- Optimized storage – Where data is being store should be identified as well as how they are synced and distributed; data that can be moved to the cloud should be, which will liberate space onsite for the most recent data available.
- Classified data – Data should be grouped into different sections based on how it will be used, who will be able to access it, its required level of confidentiality and requisite security policies. The format of the data and whether it can be changed to structured data are two other factors medical organizations should consider.
- Ordering unstructured data – Normalizing unstructured data for clinical or business value is another good step to take. This can be done with the use of natural language processing (NLP) and AI.
- Identifying context – NLP can help to normalize this data, but it will need a human perspective on the information to ensure that context is still taken into consideration.
- Follow industry standards when coding – Once the context of the data is understood, all relevant information from healthcare data should be coded to industry standards such as ICD-10 or SNOMED. This also helps with the structuring process as the code will help to make it readable and useful for analytics and machine learning models.
- Collaboration between teams – Facilities must ensure that the data scientists helping with the transition to data management have help from staff with clinical backgrounds; these employees should provide guidance to the data scientists before they work on any given data set.
Moving Forward with Data Management
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, using real-time data management and analysis to improve patient care is becoming a crucial step for healthcare facilities. It transforms their day-to-day processes and enables them to look for ways to enhance future care and influence current clinical events as they unfold.




